From Garden to Glory: How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings for a Vibrant Display, this guide explores the art of cultivating roses from cuttings, offering a rewarding journey from simple stems to breathtaking blooms. Roses, with their enduring popularity and captivating beauty, have graced gardens and hearts for centuries.
Their symbolic significance and vibrant colors make them a cherished addition to any landscape. But beyond their visual appeal lies the fascinating world of rose propagation, a practice that allows gardeners to expand their collections and create vibrant displays.
This article delves into the techniques of rose propagation, providing a step-by-step guide that empowers you to transform cuttings into thriving rose bushes. From selecting the perfect cuttings to nurturing their growth, you’ll learn the secrets to success, ensuring your garden is adorned with the exquisite beauty of roses.
The Allure of Roses
Roses, with their captivating beauty and intoxicating fragrance, have long held a special place in the hearts of gardeners and admirers alike. Their enduring popularity spans centuries, making them a timeless symbol of love, beauty, and passion. Roses have a rich history, dating back thousands of years.
They were cultivated in ancient civilizations like Egypt, Greece, and Rome, where they were revered for their medicinal properties and aesthetic appeal. In ancient China, roses were prized for their fragrance and used in perfumes and teas. The rose’s journey through time is marked by its significance in various cultures and religions.
Cultural Symbolism and Significance
Roses have deep cultural symbolism, often representing different emotions and ideas. The color of the rose plays a crucial role in conveying its meaning.
Just like propagating roses from cuttings can create a stunning display of blooms, you can also easily expand your garden with vibrant clematis vines. For a comprehensive guide on mastering this technique, check out How to Make Clematis Propagation Easy and Effective.
These methods, whether for roses or clematis, will help you cultivate a thriving and visually captivating garden.
- Red roses are traditionally associated with love, passion, and romance.
- White roses symbolize purity, innocence, and new beginnings.
- Yellow roses represent friendship, joy, and happiness.
- Pink roses are often linked to gratitude, appreciation, and admiration.
Roses have also played a significant role in literature, art, and mythology. In Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet, the rose is a symbol of love and passion. In Greek mythology, the rose is associated with Aphrodite, the goddess of love and beauty.
Diversity and Visual Appeal
The world of roses is incredibly diverse, with thousands of varieties, each with its unique characteristics. From the classic hybrid tea roses with their large, perfectly formed blooms to the rambling roses that cascade over walls and fences, there is a rose for every garden style and preference.
Roses come in a wide array of colors, from vibrant reds and yellows to delicate pinks and whites. There are even roses with bi-colored petals, creating a stunning visual effect.
The Art of Rose Propagation

Rose propagation is a rewarding and accessible endeavor, offering a chance to expand your rose garden with new varieties and enjoy the satisfaction of cultivating your own blooms. While purchasing rose plants is a convenient option, propagating roses from cuttings offers distinct advantages, including the ability to multiply your favorite varieties, preserve unique cultivars, and enjoy the thrill of witnessing a new rose plant emerge from a simple cutting.
Advantages of Propagating Roses from Cuttings
Propagating roses from cuttings offers several advantages over other methods, such as:
- Cost-Effectiveness:Propagating roses from cuttings is significantly more economical than purchasing new rose plants, allowing you to expand your garden without breaking the bank.
- Preservation of Unique Varieties:This method allows you to preserve rare or cherished rose varieties that may not be readily available commercially.
- Enhanced Disease Resistance:Rose cuttings often inherit the disease resistance of the parent plant, making them more resilient and less prone to common rose ailments.
- Increased Genetic Diversity:Propagating from cuttings introduces new genetic variations into your rose garden, promoting diversity and resilience.
- Personal Satisfaction:The process of nurturing a rose cutting into a thriving plant is deeply rewarding and fosters a deeper connection with your garden.
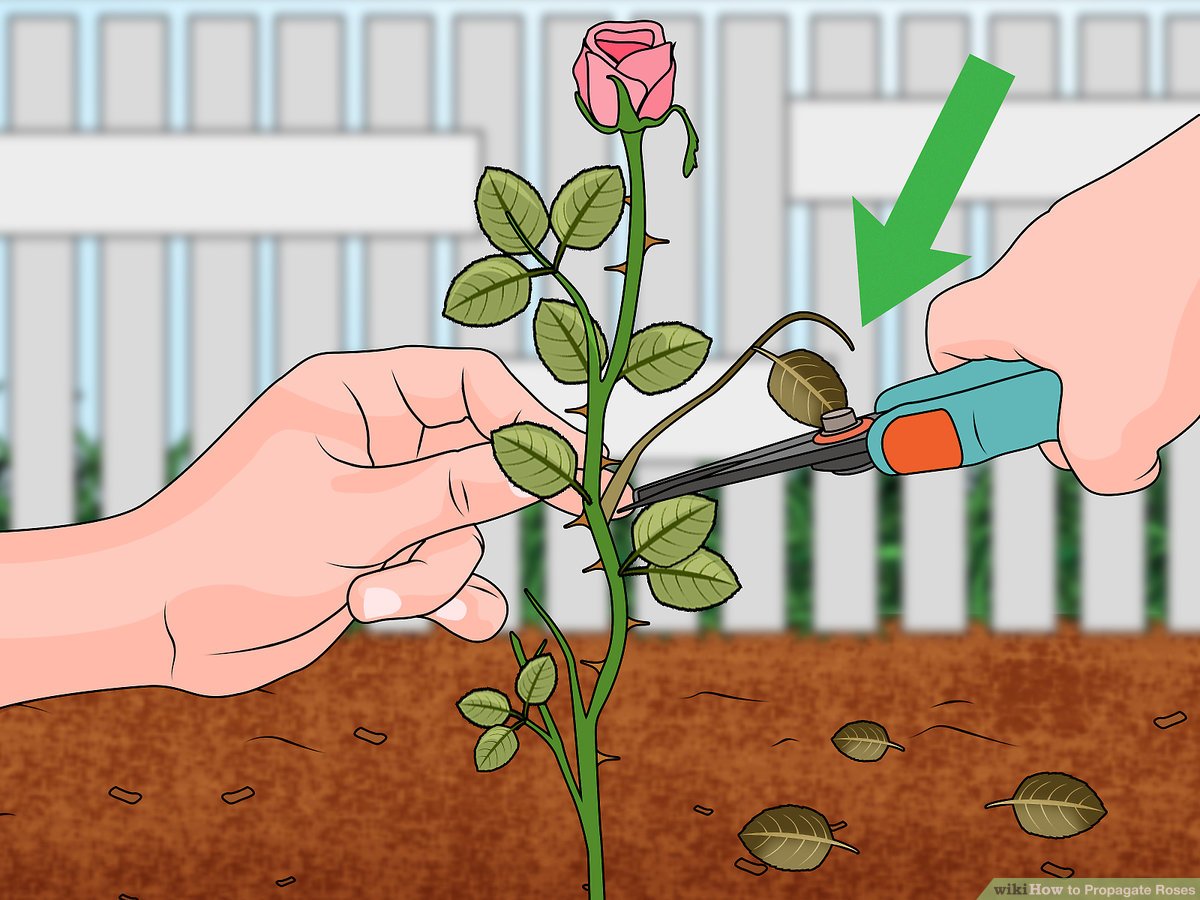
Taking Rose Cuttings
The process of taking rose cuttings involves selecting the right cutting, preparing it for propagation, and providing the ideal conditions for root development.
Ideal Time for Taking Cuttings
- Late Spring:The period after the first flush of blooms, when the rose bush is actively growing, is an ideal time for taking cuttings. The new growth is soft and pliable, making it easier to root.
- Early Summer:The summer months, when the rose bush is still producing new growth, are also suitable for taking cuttings.
- Late Summer:The late summer months, before the onset of colder temperatures, can be a good time for taking cuttings from semi-hardwood growth, which is slightly more mature and less prone to wilting.
Selecting the Right Cutting
- Choose Healthy Growth:Select a stem that is free of disease, pests, and any signs of damage.
- Look for New Growth:Choose a stem from the current year’s growth, as this is the most vigorous and easiest to root.
- Avoid Flower Buds:Cuttings with flower buds are less likely to root successfully, as they divert energy to bloom production.
- Consider the Cutting Length:Aim for a cutting that is approximately 6-8 inches long.
Tools and Materials for Rose Propagation
Rose propagation requires a few essential tools and materials to ensure success.
Tool/Material |
Description |
|---|---|
Sharp Pruning Shears or Knife |
For making clean, precise cuts. |
Rooting Hormone Powder or Gel |
To stimulate root growth and protect the cutting from fungal infections. |
Clean Pots or Containers |
For planting the cuttings. Choose pots with drainage holes. |
Potting Mix |
Use a well-draining potting mix specifically designed for rooting cuttings. |
Water |
For keeping the potting mix moist. |
Greenhouse or Propagator |
To provide a warm, humid environment for the cuttings to root. |
Preparing the Cuttings
The success of rose propagation through cuttings hinges on proper preparation. This involves selecting the right cuttings, cleaning them, making precise cuts, and treating them to encourage root development.
Cleaning and Trimming
Rose cuttings should be taken from healthy, disease-free stems. Begin by removing any leaves below the intended cutting point. These leaves will rot and introduce bacteria, hindering root growth.
Treating Cuttings
Rose cuttings benefit from a treatment with rooting hormone, a powdered or liquid solution containing plant hormones that stimulate root development. This process is vital for promoting root growth, especially in challenging conditions.
Using rooting hormone is not mandatory, but it significantly increases the success rate of propagation.
- Powdered Rooting Hormone:Apply a thin layer of powdered rooting hormone to the cut end of the stem. This method is effective for most rose cuttings.
- Liquid Rooting Hormone:Dip the cut end of the stem in a liquid rooting hormone solution for a few seconds. This method is ideal for larger cuttings.
Rooting Medium
The rooting medium plays a crucial role in the success of rose propagation. It should be well-draining, provide good aeration, and retain moisture.
- Potting Mix:A commercially available potting mix specifically formulated for rooting cuttings is an excellent choice.
- Perlite:This lightweight, porous material provides excellent drainage and aeration. It can be mixed with potting mix for improved rooting conditions.
- Vermiculite:Similar to perlite, vermiculite offers good moisture retention and aeration. It is also beneficial for its ability to retain nutrients.
Nurturing New Growth

The success of your rose propagation journey hinges on providing the right environment for your cuttings to develop roots and flourish. After meticulously preparing your cuttings, it’s time to create a nurturing haven that encourages new growth. This section will guide you through the process of planting your cuttings, maintaining them, and creating a mini-greenhouse for optimal growth.
Planting Rose Cuttings
Planting your rose cuttings in a suitable environment is crucial for their successful rooting. Choose a well-draining potting mix that retains moisture but doesn’t become waterlogged. A mixture of peat moss, perlite, and vermiculite is ideal. The pot should be deep enough to accommodate the length of the cutting, with drainage holes to prevent root rot.
To plant your cuttings, make a small hole in the potting mix, insert the cutting, and gently firm the soil around it. Ensure that the bottom node (the point where the leaves grow) is buried in the soil.
Similar to the success of propagating roses from cuttings, you can also achieve a vibrant display of lush foliage by growing new Schefflera plants from cuttings. For a comprehensive guide on this process, check out The Complete Guide to Growing New Schefflera Plants from Cuttings , which details the steps for successful propagation.
Once you’ve mastered the art of propagating Schefflera, you’ll be well on your way to creating a beautiful and flourishing garden filled with roses and other vibrant greenery.
Care Tips for Rose Cuttings
Maintaining your rose cuttings requires consistent attention to ensure they receive the right amount of water, humidity, and light. Here are essential care tips:
Watering
- Keep the potting mix consistently moist, but not soggy. Water thoroughly, allowing excess water to drain out.
- Avoid overwatering, as this can lead to root rot.
- Water in the morning to allow the soil to dry slightly before nightfall.
Humidity Control
- Rose cuttings thrive in humid environments.
- Create a humid environment by placing the cuttings in a plastic bag or a mini-greenhouse.
- Regularly mist the cuttings with water to maintain humidity levels.
Light Exposure
- Rose cuttings require bright, indirect light for photosynthesis.
- Place them in a location that receives ample sunlight, but avoid direct sunlight, which can scorch the leaves.
- During the winter months, supplement with artificial light to ensure sufficient light exposure.
Creating a Mini-Greenhouse
A mini-greenhouse or propagation chamber provides an ideal environment for rose cuttings to root. You can easily create one using readily available materials:
Materials
- A clear plastic container with a lid (such as a storage container or a large Tupperware)
- Potting mix
- Rose cuttings
- Water
Instructions
- Fill the container with potting mix, leaving a few inches of space at the top.
- Make holes in the potting mix and insert your prepared rose cuttings.
- Gently water the cuttings.
- Place the lid on the container, creating a sealed environment.
- Place the container in a bright, indirect light location.
- Monitor the cuttings regularly, misting them with water as needed to maintain humidity levels.
From Roots to Blooms: From Garden To Glory: How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings For A Vibrant Display
Patience and care are essential as you watch your rose cuttings transition from dormant stems to thriving plants. This chapter explores the signs of successful rooting, the gradual acclimatization process, and crucial tips for nurturing young rose plants to achieve abundant blooms.
Signs of Successful Rooting and Timeline for New Growth
The emergence of new growth is a clear indication that your rose cuttings have successfully rooted. This typically occurs within 4 to 8 weeks, depending on the variety of rose and the environmental conditions. Here are some signs to look for:
- New Leaf Buds:Tiny, green buds will appear at the nodes, indicating the plant is drawing nutrients from its newly formed roots.
- Firm Stems:The stems will become firmer and more robust, suggesting the roots are providing adequate support.
- Root Development:If you gently tug on the cutting, you should feel resistance, signifying the roots are anchoring the plant in the rooting medium.
Gradual Acclimatization to Outdoor Conditions
Once your rose cuttings have established a strong root system, they need to be gradually acclimatized to outdoor conditions to avoid shock and ensure their survival. This process involves exposing them to increasing amounts of sunlight and wind over a period of several weeks.
- Start with Shade:Initially, place the potted cuttings in a shaded location for a few hours each day, gradually increasing the exposure time over the next week.
- Introduce Direct Sunlight:After a week of shade acclimatization, start exposing the cuttings to direct sunlight for a few hours each day, again gradually increasing the exposure time over the next week.
- Wind Protection:Provide protection from strong winds, especially during the initial stages of acclimatization. A sheltered spot or a windbreak can help.
Nurturing Young Rose Plants for Healthy Growth and Abundant Blooms
Once your rose cuttings have successfully transitioned to outdoor conditions, providing proper care is crucial for healthy growth and abundant blooms. This involves consistent watering, fertilization, and pest control.
- Watering:Water the plants regularly, especially during dry periods, ensuring the soil is consistently moist but not waterlogged.
- Fertilization:Apply a balanced fertilizer specifically formulated for roses every 4-6 weeks during the growing season. This provides the essential nutrients for healthy growth and flowering.
- Pest Control:Regularly inspect the plants for signs of pests such as aphids, spider mites, and rose slugs. Treat any infestations promptly with appropriate pest control methods.
Designing a Vibrant Display
Propagating your own roses opens up a world of possibilities for creating a stunning and personalized garden display. With a little planning and creativity, you can arrange your newly propagated roses to enhance the beauty of your outdoor space.
Rose Variety Placement
Choosing the right location for each rose variety is crucial for maximizing their growth and showcasing their unique characteristics. Here’s a table highlighting the ideal placement of different rose types within a garden:
Rose Variety |
Ideal Placement |
Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
Climbing Roses |
Trellises, Walls, Arbors |
Provide vertical support and create a dramatic, cascading effect. |
Shrub Roses |
Borders, Foundation Plantings |
Offer a full, rounded shape and add color and texture to garden edges. |
Miniature Roses |
Rock Gardens, Containers |
Compact size makes them perfect for small spaces and containers. |
Hybrid Tea Roses |
Focal Points, Cut Flower Gardens |
Known for their large, showy blooms and long stems, ideal for bouquets. |
Floribunda Roses |
Mass Plantings, Beds |
Produce clusters of smaller blooms, creating a vibrant and colorful display. |
Companion Planting, From Garden to Glory: How To Propagate Roses From Cuttings for a Vibrant Display
Companion planting involves strategically pairing roses with other plants to create a harmonious and beneficial ecosystem. This practice can enhance rose health, attract beneficial insects, and deter pests.
“Roses benefit from companion planting with herbs like rosemary, lavender, and thyme, which repel pests and improve soil drainage.”
- Herbs: Rosemary, lavender, thyme, and sage repel pests and improve soil drainage.
- Annuals: Marigolds, zinnias, and cosmos attract beneficial insects and add visual interest.
- Vegetables: Onions, garlic, and carrots deter pests and improve soil fertility.
Conclusive Thoughts

By embracing the art of rose propagation, you unlock a world of possibilities, transforming your garden into a fragrant sanctuary. From the initial selection of cuttings to the joy of witnessing their transformation into blooming rose bushes, this journey is both rewarding and empowering.
With patience and care, you can cultivate a vibrant display of roses that will grace your garden for years to come, adding a touch of elegance and beauty to your outdoor oasis.
Detailed FAQs
How long does it take for rose cuttings to root?
Rose cuttings typically take 4 to 8 weeks to develop roots, depending on factors like the variety, climate, and care provided.
What are the best rose varieties for propagation?
Hybrid tea roses, floribunda roses, and grandiflora roses are generally good choices for propagation. These varieties tend to root readily and produce beautiful blooms.
Can I propagate roses from store-bought flowers?
It’s possible to propagate roses from store-bought flowers, but success is less guaranteed. The flowers might have been treated with chemicals that hinder rooting.
What is the best time of year to take rose cuttings?
The ideal time to take rose cuttings is during the dormant season, typically in late fall or early spring. This is when the plant’s energy is focused on the roots, promoting successful rooting.